Thoracic Spondylosis ICD 10: Complete Guide to M47.814 and Related Thoracic Codes
Thoracic spondylosis is a degenerative condition affecting the mid-back region, often causing stiffness, discomfort, and limited mobility in the thoracic spine. Accurate coding with Thoracic Spondylosis ICD 10 is vital for healthcare documentation, ensuring correct billing and precise tracking of patient diagnoses. Using the right code enables clinicians and coders to maintain clarity and support effective patient care management.
Understanding Thoracic Spondylosis ICD 10 also aids in research, allowing health systems to monitor the prevalence and impact of thoracic spinal conditions. Accurate coding ensures data consistency across clinical settings and improves communication between healthcare professionals. For medical coders and clinicians alike, mastering Thoracic Spondylosis ICD 10 is essential for delivering high-quality care and maintaining regulatory compliance.
Understanding Thoracic Spondylosis
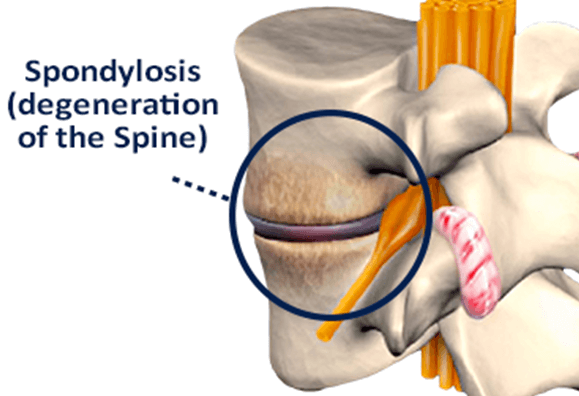
Thoracic spondylosis refers to the natural degeneration of the thoracic spine, including the vertebrae, intervertebral discs, and facet joints. Common causes include ageing, repetitive spinal stress, and genetic predisposition. Symptoms often include back stiffness, chronic pain, and sometimes neurological signs such as tingling, numbness, or weakness. Myelopathy and radiculopathy may occur if nerve involvement develops, making accurate diagnosis and coding with Thoracic Spondylosis ICD 10 critical.
Risk factors such as a sedentary lifestyle, obesity, poor posture, and previous spinal injuries can accelerate the progression of thoracic spondylosis. Unlike cervical or lumbar spondylosis, thoracic spondylosis is less frequently diagnosed but can significantly affect mobility and quality of life. Correctly documenting the condition with Thoracic Spondylosis ICD 10 ensures proper treatment planning and facilitates research into effective management strategies for spinal degeneration.
Thoracic Spondylosis ICD 10 Codes
The Thoracic Spondylosis ICD 10 classification provides a structured system for documenting different types of spondylosis in the thoracic region. The most commonly used code is M47.814, which represents spondylosis without myelopathy or radiculopathy. M47.14 is designated for cases where myelopathy, or spinal cord compression, is present, while M47.24 is used for radiculopathy, reflecting nerve root involvement. M47.894 covers other, unspecified thoracic spondylosis cases.
Choosing the correct Thoracic Spondylosis ICD 10 code requires careful evaluation of clinical findings, imaging studies, and patient-reported symptoms. Misclassification can lead to insurance claim denials and inaccurate medical records. Healthcare professionals must cross-reference patient documentation with ICD-10 guidelines to select the most precise code. Proper use of Thoracic Spondylosis ICD 10 ensures accurate reporting, supports research, and maintains compliance within the healthcare system.
How to Accurately Code Thoracic Spondylosis
Accurate coding of thoracic spondylosis involves detailed review of patient history, imaging results, and neurological examinations. Identifying whether the patient has myelopathy or radiculopathy is essential for selecting the correct Thoracic Spondylosis ICD 10 code. Proper coding enables clinicians to provide targeted treatment while ensuring medical records remain precise and comprehensive.
Common coding errors often arise when unspecified codes are used instead of more specific options like M47.814. Coders should verify details such as the presence of nerve involvement or localisation to the thoracic region. Adhering to Thoracic Spondylosis ICD 10 guidelines reduces errors, supports insurance processes, and enhances overall patient care. Accurate documentation ensures a smooth workflow for healthcare professionals and reliable statistical tracking for clinical studies.
ICD-10 vs ICD-11 for Thoracic Spondylosis
While ICD-11 offers updated terminology and more detailed classifications for spinal conditions, Thoracic Spondylosis ICD 10 remains the standard in many UK healthcare settings. Transitioning to ICD-11 requires understanding code equivalents, additional subcategories, and clinical training for coders. Despite updates, Thoracic Spondylosis ICD 10 codes continue to be essential for daily documentation and historical data analysis.
ICD-11 provides expanded details for nerve involvement, spondylosis subtypes, and degenerative changes. However, the familiarity and widespread use of Thoracic Spondylosis ICD 10 make it indispensable for clinical documentation, insurance reporting, and research purposes. Clinicians must balance using the updated ICD-11 system while ensuring consistent Thoracic Spondylosis ICD 10 coding for comparability and continuity of patient records.
Treatment and Management of Thoracic Spondylosis
Treatment for thoracic spondylosis focuses on symptom relief, improving spinal function, and preventing progression. Conservative approaches include physiotherapy, targeted exercises, pain management, and lifestyle modifications such as posture correction and weight management. Accurate Thoracic Spondylosis ICD 10 coding ensures that treatments are documented correctly and helps track patient outcomes.
In severe cases, where myelopathy or radiculopathy causes significant neurological impairment, surgical intervention may be necessary. Correct use of Thoracic Spondylosis ICD 10 codes ensures appropriate treatment planning, insurance coverage, and continuity of care. Regular follow-ups and precise coding support healthcare professionals in monitoring patient progress and adjusting treatment strategies as needed.
Conclusion
Thoracic spondylosis is a complex spinal condition requiring precise diagnosis and meticulous documentation. Using Thoracic Spondylosis ICD 10 codes, particularly M47.814, ensures accurate reporting, supports insurance claims, and facilitates research into spinal degenerative diseases. Understanding and applying these codes correctly is essential for clinicians, coders, and healthcare administrators in the UK, promoting effective patient management and high-quality care.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the ICD-10 code for thoracic spondylosis?
The primary code is M47.814 for thoracic spondylosis without myelopathy or radiculopathy.
How can clinicians determine if thoracic spondylosis involves myelopathy or radiculopathy?
Through clinical examination, imaging, and neurological assessments.
Are Thoracic Spondylosis ICD 10 codes applicable to all patients in the UK?
Yes, these codes are standard for documentation in UK healthcare settings.
What is the difference between M47.814 and M47.14?
M47.814 is without nerve involvement, while M47.14 indicates myelopathy.
How is thoracic spondylosis diagnosed and managed in the UK?
Diagnosis is via imaging and clinical assessment; management includes physiotherapy, medication, or surgery.
Does the ICD-10 code affect treatment options or insurance claims?
Yes, accurate coding ensures proper treatment documentation and insurance processing.
How does ICD-11 differ from Thoracic Spondylosis ICD 10 in classification and use?
ICD-11 provides more detailed categories, but ICD-10 remains widely used for UK records.
You May Also Read: Kings Theatre Portsmouth Parking and Accessibility